Once you learn how to trade forex, you’ll understand why it’s such a popular market. You’ll discover that you can choose between many different currency pairs – from majors to exotics – and trade 24 hours a day. Use this guide to learn how to trade currency with our FX trading steps and examples. Interested in trading forex with us?

Choose a currency pair to trade
We offer more than 80 currency pairs – from majors like GBP/USD, to exotics like HUF/EUR. When you trade with us, you’ll be speculating on these forex pairs rising or falling in value with spread bets and CFDs. These make use of leverage, which enables you to open a larger forex trade with a small upfront deposit (called margin). However, this means your losses as well as profits can far outweigh your margin amount as they are calculated based on the full position size, not just your margin.
Before choosing an FX pair to trade, you should carry out fundamental analysis and technical analysis on the two currencies in the pair. This means you should assess how the ‘base’ (the currency on the left) and the ‘quote’ (the currency on the right) move in relation to each other.

Decide whether to ‘buy’ or ‘sell’
Once you’ve chosen a currency pair to trade, you need to decide whether you want to ‘buy’ or ‘sell’, based on your analysis.
You would buy the pair if you expected the base currency to rise in value against the quote currency. Or, you would sell if you expected it to do the opposite. That’s because a currency pair’s price represents how many of the quote currency you’d have to spend to buy a single unit of the base currency.
For example if the price quoted for GBP/USD is 1.28000, it means you’d have to spend $1.28 to buy £1 – so the pound is stronger than the US dollar.
Set your stops and limits
The forex market is particularly volatile, which is why it’s important to have a plan to guide the entry and exit points of your trades. There are various stops and limits you can set to manage your risk when trading forex:


Normal stops will close your position automatically if the market moves against you. Note that normal stops do not protect against slippage.
Guaranteed stops will always be closed out at exactly the price you specified – even if the market moves quickly or ‘gaps’. You’ll pay a small premium if a guaranteed stop is triggered


Trailing stops will follow positive price movements and close your position if the market moves against you
Limit orders can help you to achieve your profit target, and your position will be closed when the price hits your chosen level
Open your first trade
If you want to trade on the value of forex pairs rising or falling with spread bets or CFDs, why not open an account with us? Once you’ve done that, simply go to our award-winning trading platform,1 search for the forex pair you want to trade, enter your position size and choose ‘buy’ or ‘sell’.
There’s no obligation to add funds until you want to place a trade.
Monitor your position
Once you’ve opened your position, you can monitor your FX trade in the ‘open positions’ section of the dealing platform. You can also set price alerts to receive email, SMS or push notifications when a specified buy or sell percentage or point is reached.
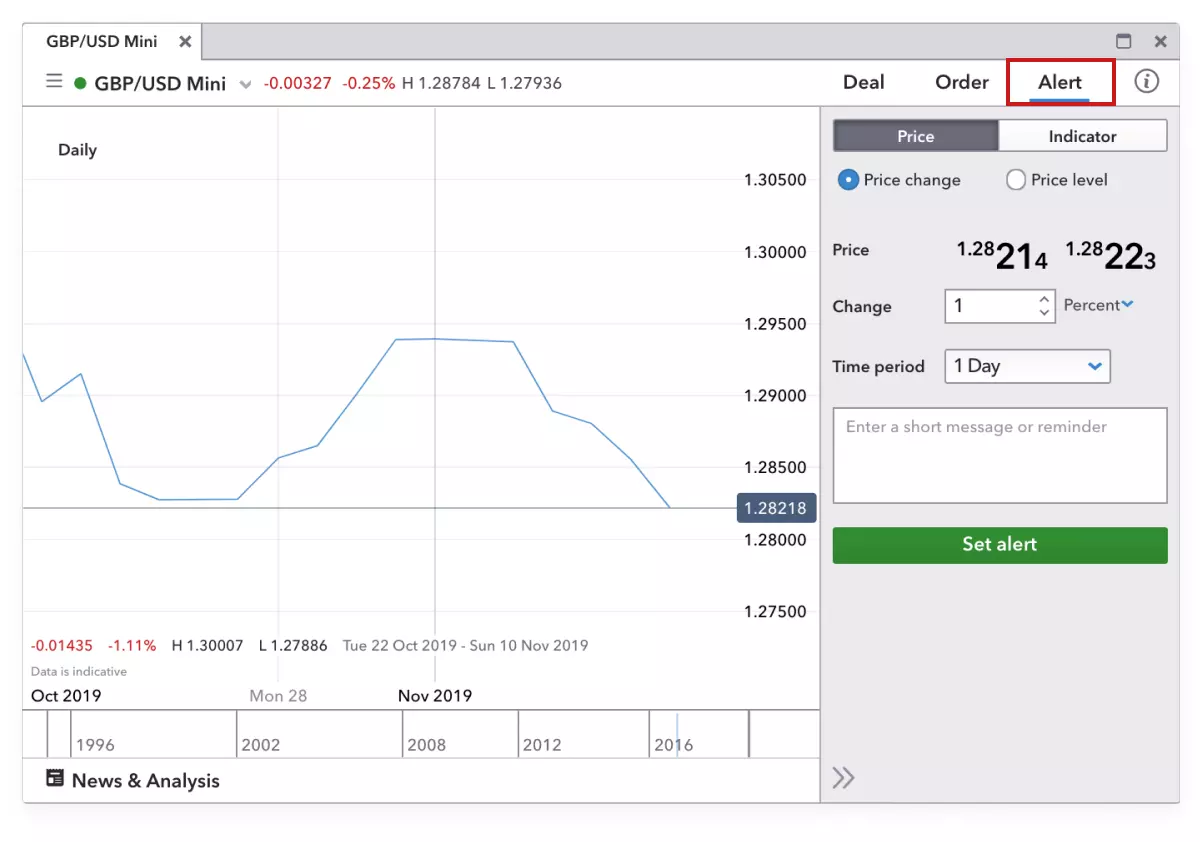
Even with these alerts set, it’s still important to keep up to date with the latest news and political events that could move the forex market.
Close your trade and take your profit or loss
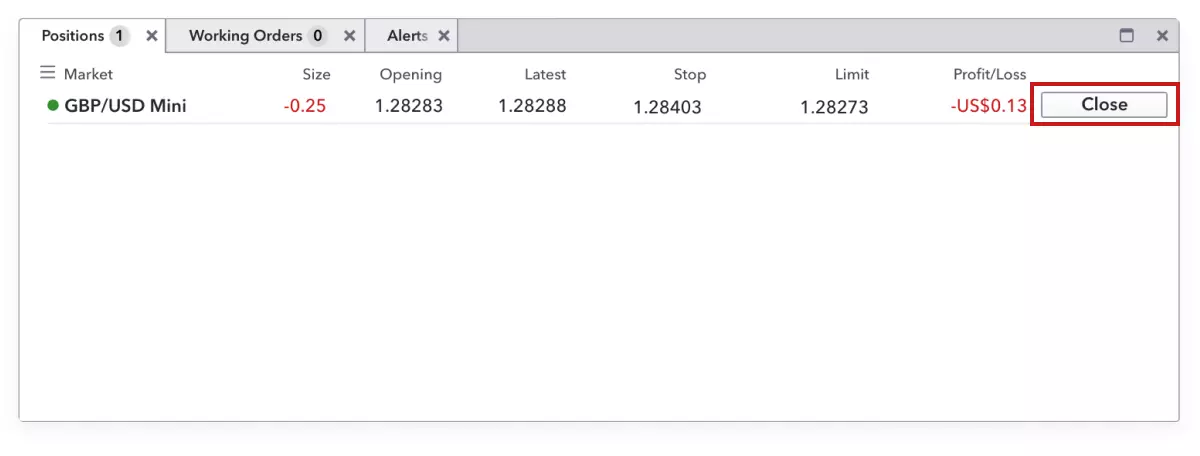
Once you’ve decided it’s time to close your position, simply navigate to the ‘positions’ tab, select your position and click on ‘close’. Alternatively, just make the opposite trade to the one you opened. In other words, if you went long on GBP/USD, go short by an equivalent amount to close the position – assuming you’ve selected the ‘net-off’ option on our platform, rather than ‘force open’.
Forex trading examples
We’ve included an example of a forex spread bet and a forex CFD trade below.
- Forex spread bet
- Forex CFD trade
Forex spread bet
Forex spread betting lets you make a prediction on the direction in which a forex pair’s price is heading. You’ll bet an amount of money per point of movement, and if the price moves in the same direction that you predicted, the greater your profit. But, the further it moves in the opposite direction, the greater your loss.
Forex spread bets are also leveraged. This means that you’ll pay a small margin when opening a trade but gain exposure to the total position size. However, it also means your losses and profits can far outweigh your deposit amount.
Spread bet prices are displayed in points – for example, if GBP/USD is trading at $1.31425, its price would be displayed as 13142.5. This makes no difference to the price you deal at or your potential profit or loss: it simply makes it easier to track per-point movements. When you trade forex with spread bets, all of your profits are completely tax-free.2
Forex CFD trade
When you trade forex CFDs, you’re agreeing to exchange the difference in the price of a position from the point at which it is opened up until it is closed. To open this position, you’ll pay a small margin upfront to gain exposure to the larger position. However, this means your losses as well as profits can far outweigh your deposit amount. CFD prices are displayed in the same way as a regular forex pair’s quote price – for example 1.31425.
Plus, you’ll be able to speculate on prices rising by going long, as well as falling by going short. Standard forex CFDs are worth 100,000 units of the first named currency in the pair, while mini forex CFDs are worth just 10,000 units of the same. CFDs are liable to capital gains tax, but you can offset your losses against profits for tax purposes.2
FAQs
What are the differences between forex CFDs and spread bets?
- Trading forex CFDs means you’re agreeing to exchange the difference in price of a forex pair from the point at which the CFD is opened, to the point at which it’s closed
- Forex spread betting means you’re betting an amount of money per point of movement in the underlying currency pair’s price
But, there are other differences between spread bets and CFDs that you should take time to familiarise yourself with.
How much money do I need to start trading forex?
You only need to put down a small deposit (usually 3.33% of the total position size) when you trade forex with derivatives, because you’ll be trading with leverage. But, while that’s all you need to start trading, remember that profits and losses will be calculated using the full size of the position – so you should ensure that you can cover the downside if the market moves against you.
What do I need to start trading forex?
Once you have established how much capital you have available, you will then need to start preparing the rest of your forex trading plan – this should include what you want to get out of trading forex, the time you are willing to commit to trading, researching which markets you want to trade, your risk management strategy and your trading strategy.
Can anyone trade forex?
Anyone can trade forex if they develop their trading knowledge, build a forex trading strategy and gain experience trading the market. But, the volatility of the forex market is a unique environment that takes time to understand.
What is a good forex trading strategy?
A forex trading strategy should consider the trading style that best suits your goals and time commitments. For example, a day trading strategy involves opening and closing positions within a single trading day, taking advantage of small intraday movements in a currency pair’s price.
What currency pairs move the most?
The forex market is extremely volatile, so a currency pair that moves up one week might go down the next. But, the majority of forex trading volume is concentrated in a handful of forex pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD and USD/CHF.
That’s because these pairs represent some of the most widely-circulated currencies and so they attract the most traders. This results in a greater amount of price movement as the balance between buyers and sellers constantly shifts.
Develop your forex knowledge with IG
Find out more about forex trading and test yourself with IG Academy’s range of online courses.
Try these next
Learn more about spread betting with IG
Be aware of the risks associated with forex trading and understand how IG supports you in managing them
Discover the different platforms that you can trade forex with IG
1 Awarded UK’s best trading platform at the ADVFN International Financial Awards 2020 and Professional Trader Awards 2019.
2 Tax laws are subject to change and depend on individual circumstances. Tax law may differ in a jurisdiction other than the UK.
