How to trade or invest in natural gas
Natural gas is one of the most commonly-traded commodities out there. Being highly volatile, it presents plenty of opportunities for traders. Find out how to trade natural gas, what affects its price and some useful strategies.

Natural gas trading and investing basics
Natural gas is currently the third most used form of energy to generate power, representing 24% of globally generated power in 2021.1 The popularity of natural gas has been maintained by its increased use in developing countries like China and Indonesia.
Natural gas is used to heat buildings, boil water, fuel vehicles, cook food, run air conditioning units and power industrial furnaces. Household appliances like a gas hob or a house’s radiators function by turning the energy supplied by natural gas into heat.
Henry Hub Natural Gas (NG) futures are the industry benchmark and they are traded through the Chicago Mercantile Exchange Group (CME Group). The name comes from the Henry Hub, a natural gas pipeline in Louisiana which serves as the official delivery location for futures contracts. By volume, natural gas futures are the third largest physical commodity futures contract in the world.2
How to trade or invest in natural gas
With us, you can take your position on gas in a few ways. The market price is based on underlying futures prices.
- Spread betting account - you can stake an amount of money per point the market moves. If you were to go long on natural gas and put down £10 per point, you would gain £10 for every point natural gas rose in price, or lose £10 for every point it fell
- CFD trading account - you exchange the difference in price between when you open and close your position. Our natural gas CFD markets work similarly to spread bets, because each contract is worth a set amount (for example, £1 per contract). So if your position size were £10 and the contract size were £1, here you'd also gain or lose £10 per point depending on the direction of the market
- Share dealing account - you buy or sell ETFs, ETCs, or shares linked to natural gas markets
With both spread betting and CFDs, you're trading on leverage. This means you could gain or lose money faster than you'd expect, because your position size is greater than the money your initial deposit.
When spread betting or trading CFDs you can either trade our 'undated' natural gas spot markets, or natural gas futures. When you trade on the spot, you trade closer to the current price and with tighter spreads. However, you need to be aware of overnight fees. When trading futures, you'll find larger spreads but you won't pay any overnight fees.
You can take your position on Natural Gas or UK Natural Gas.
When you deal shares, you buy and own the stock. Oil majors, like BP PLC and Shell PLC are investing resources in natural gas, so you could buy their shares as a play on this theme.
Braver investors may prefer to look for exploration companies that are directly engaged in fracking. These could include UK oil and gas extractor and developer IGAS Energy PLC, or Egdon Resources PLC, another British firm focusing on UK-based onshore production and exploration.
There are also ETFs and ETCs linked to natural gas which you can find on our platform.
What moves the price of natural gas?
As with most commodities, the price of natural gas is driven by supply and demand. Some of the key factors affecting supply and demand for natural gas are the stored reserves, global demand, development of alternative fuels, prices of alternative fuels and the weather.
Essentially, if more people want to buy natural gas than sell it, the price will rise because it is more sought-after (the ‘demand’ outstrips the ‘supply’). On the other hand, if supply is greater than demand, the price will fall.
Global demand
Global demand for natural gas is expected to remain subdued up to 2025. Russia's invasion of Ukraine has exacerbated the tightening supply of gas.3
Stored reserves of natural gas
Many countries around the world have stores of natural gas which they can use in the event of a supply glut. By storing natural gas, governments hope to alleviate some of the problems associated with increased prices in times of reduced production.
By keeping stores of natural gas, countries will not need to buy as much during a supply shortage, which would keep demand low for a brief period. However, once a country’s reserves run out or run low, they will need to buy more which in the case of a shortage, means higher prices in lieu of reduced availability of natural gas.
Development of alternative power
The development of greener alternatives to fossil fuels could cause the price of natural gas to drop. However, it is thought that in the coming years, the global population will become less reliant on fossil fuels like natural gas.
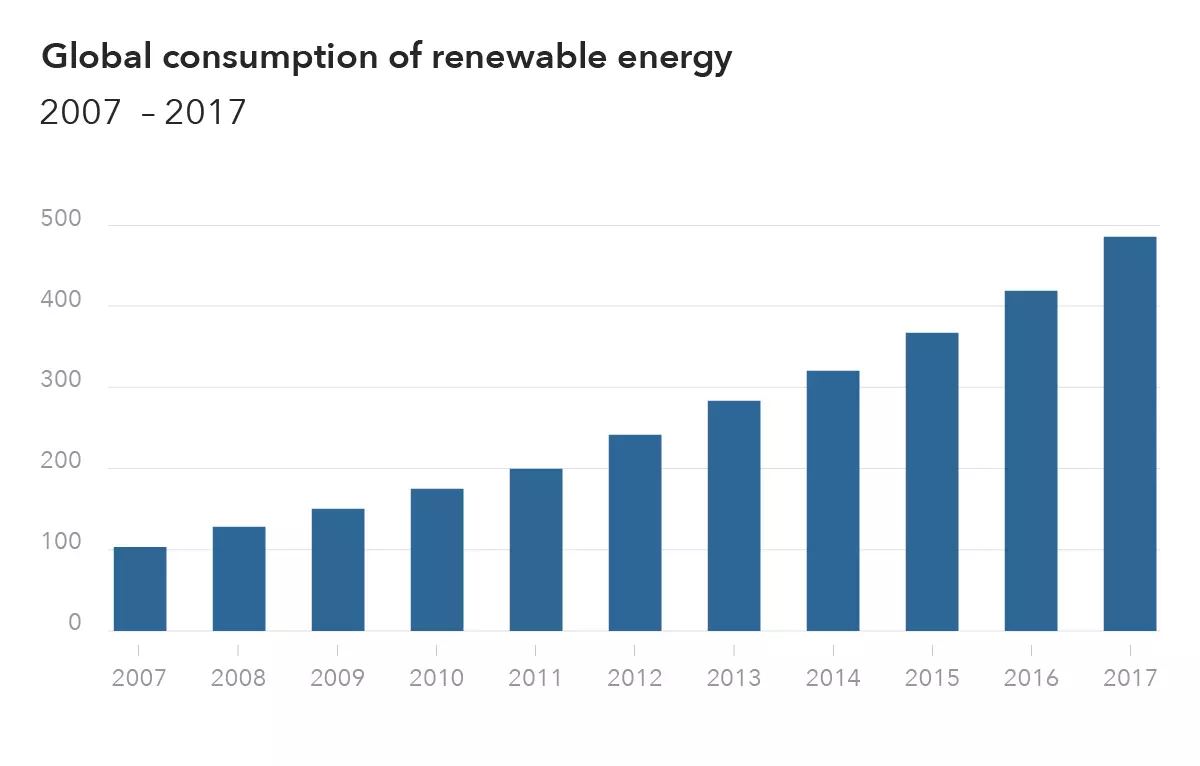
Evidence shows that global consumption of renewable energy has grown year on year, from 107 million tonnes oil equivalent in 2007 to 486.8 million tonnes oil equivalent in 2017.
Price of alternative forms of energy
If other fuels are cheaper to buy than natural gas, demand for natural gas will fall. This could happen if oil is being overproduced, or if governments dedicate more resources to building nuclear power plants and wind farms – which would reduce the price of these alternative forms of energy.
Equally, if government regulations place greater restrictions on hydraulic fracturing, it is likely that less natural gas will be extracted. Therefore, the price will increase relative to the price of other forms of energy generation such as renewable energy or nuclear power. A number of countries including Ireland, Germany, Australia, Scotland and Uruguay have already permanently or temporarily banned fracking in light of public opposition.
Weather
Severe weather, such as hurricanes and storms, can shut down natural gas production hubs for days or even weeks at a time. This means that reserves will run low as supply gets used up, which would cause the price to increase.
Equally, particularly cold winter weather could lead to more people increasing the heat in their homes. This would mean that more natural gas was being used to satisfy an increased demand which would cause its price to increase.
6 steps to trading or investing natural gas
- Learn how CFDs, spread bets and share dealing work
- Create an account and deposit your funds
- Analyse supply and demand factors in the natural gas market
- Choose the trading strategy that works best for you
- Decide what natural gas asset you want to trade or invest in
- Open, monitor and close your first position
Natural gas trading strategies
Prices for commodities that are a source of energy, such as natural gas or oil, have historically been volatile because of the numerous factors that can affect their supply and demand levels. As a result, the best trading strategies to use during your time on the natural gas market are ones which capitalise on small-time gains such as day trading – as the price can shift against you overnight in a long-term position.
Day trading strategy
Day trading can be a viable way to speculate on the price of natural gas due to the high volatility in the market. Traders who deploy a day trading strategy seek to make small profits on a lot of trades throughout the day, meaning they are constantly scanning the markets throughout a single trading session.
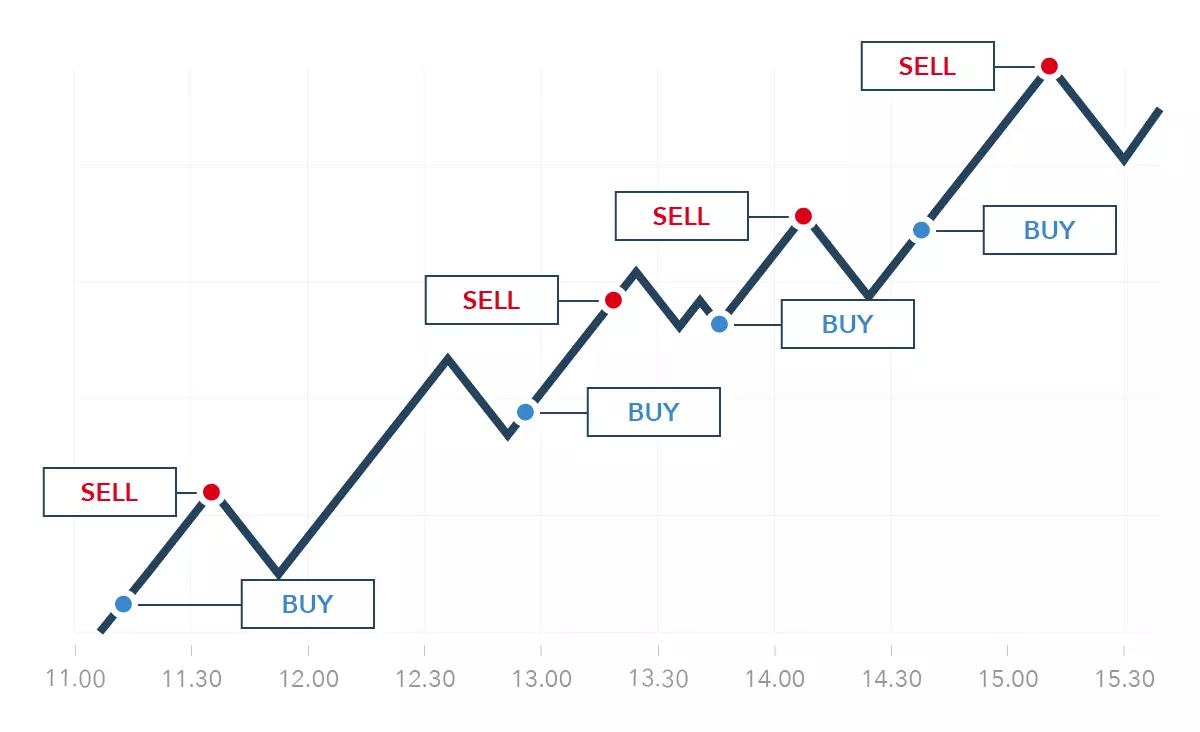
As a result, a day trading strategy is best employed by individuals who have a lot of time to commit to the markets and who can dedicate their attention to news stories and other events that could affect the price of natural gas.
Range trading strategy
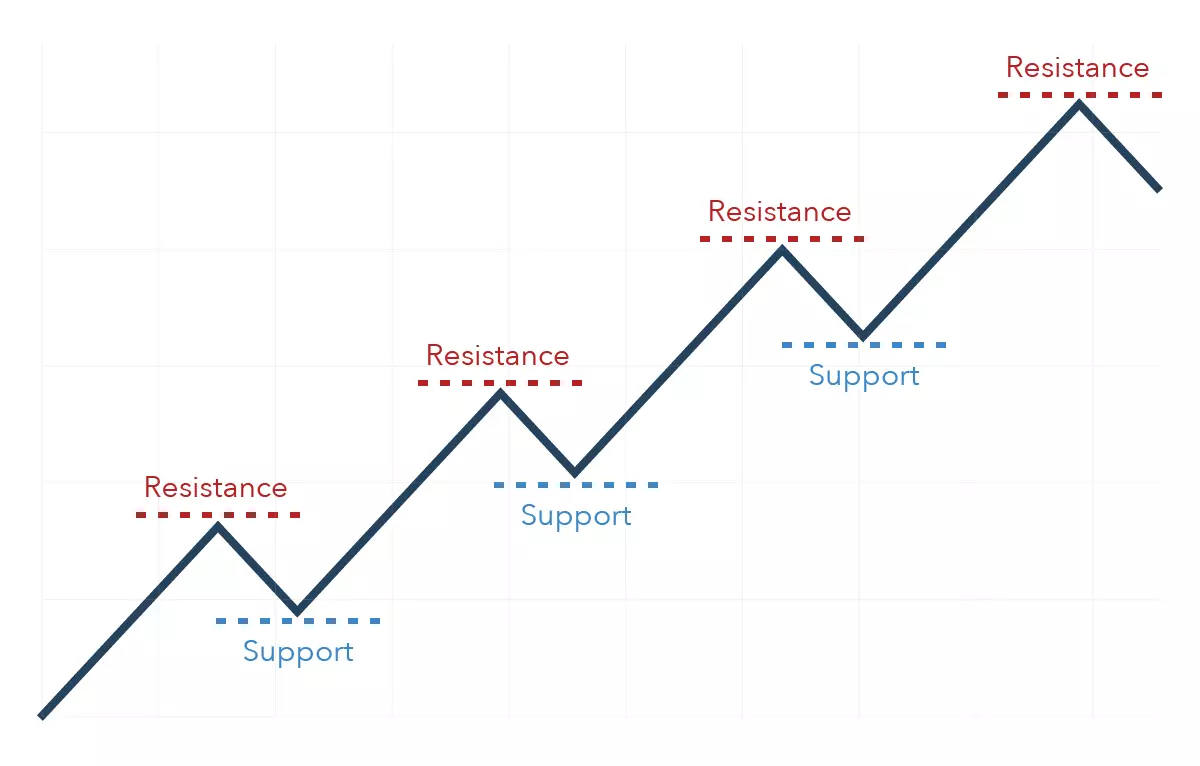
In a range trading strategy, a trader will identify levels of support and resistance in an asset’s price movements and seek to buy at levels of support and sell at levels of resistance . Range strategies work best in markets with lots of price movements where there isn’t a particular long-term trend.
This makes it a feasible strategy to use on the natural gas market, assuming that traders know how to accurately identify levels of support and resistance.
Breakout trading strategy
Breakout trading is another effective strategy to use in highly volatile markets. Its success relies on a trader spotting a price increase in the early stages of that trend. As a result, a trader will buy low and sell high, after the assets price has ‘broken’ above a level of historical resistance.
Breakout traders can also enter a short position when the price of an asset ‘breaks’ below a historical level of support; meaning that a breakout trading strategy can be used in both rising and falling markets.
Natural gas trading hours
| Location | Trading hours* |
| Chicago | 17:00 – 04:00 Sunday to Friday (Central time) |
| New York | 18:00 – 05:00 Sunday to Friday (Eastern time) |
| London | 23:00 – 10:00 Sunday to Friday (UK time) |
This information has been prepared by IG, a trading name of IG Markets Limited. In addition to the disclaimer below, the material on this page does not contain a record of our trading prices, or an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument. IG accepts no responsibility for any use that may be made of these comments and for any consequences that result. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of this information. Consequently any person acting on it does so entirely at their own risk. Any research provided does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and needs of any specific person who may receive it. It has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and as such is considered to be a marketing communication. Although we are not specifically constrained from dealing ahead of our recommendations we do not seek to take advantage of them before they are provided to our clients. See full non-independent research disclaimer and quarterly summary.

Discover how to trade the markets
Explore the range of markets you can trade – and learn how they work – with IG Academy's free ’introducing the financial markets’ course.
