For most traders and investors, an initial public offering (IPO) is the first opportunity to gain exposure to a company’s shares. Learn more about the IPO process and how to take a position with us.
What is an initial public offering (IPO)?
An initial public offering (IPO) is one of the methods that companies can use to go public – which will make its stock available to retail traders and investors. The company will decide how many shares it wants to offer, and an investment bank will suggest an initial price for the shares based on the predicted demand for them.
It should be noted that trading or investing in IPO shares can be riskier than getting exposure to established stocks, due to the unpredictability of the new listing.

Why do companies want to go public?
Companies want to go public for different reasons, depending on their circumstances. Most are looking to raise capital to fund expansion, pay debts, attract and retain talent, or monetise assets. A company may also want to list on a stock exchange to improve its public profile.
How does the IPO process work?
The IPO process starts when a company decides that it wants to sell its shares to the public via a stock exchange. First, an audit must be conducted, which considers all aspects of a company’s financials.
If everything is in order, the business then has to prepare a registration statement to file with the appropriate exchange commission, like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK.
Next, the stock exchange that the company wants to list on will review the application, after which it’s either accepted – sometimes subject to certain amendments – or rejected. If it’s approved, the company will enlist the help of an underwriter to help it decide how many shares to issue and at which price.
The underwriter is usually a bank, and it’s their job to start a book building process, looking for investors to subscribe to (register their interest in) the IPO. Any interested parties will receive a prospectus of information about the shares, where they’ll be listed and the potential opening price.
Who sets the IPO price?
Investment banks set the IPO price. The company decides how many of its shares it wants to sell to the public and then the nominated investment bank does a valuation of the business. Once that’s done, an initial share price is released, and the public can start trading shares when the listing happens.
Pros and cons of IPOs
Pros of IPOs
A successful IPO can raise huge amounts of capital, as becoming listed on a stock exchange can help to increase the exposure and public image of a company. In turn, the firm’s sales and profit can increase. IPOs are also beneficial to traders because it’s easier to buy publicly traded shares than those that only trade privately.
Cons of IPOs
Public companies are subjected to the rules and regulations of a governing body. One of the rules is that the company is required to publicly disclose financials, such as accounting information, tax and profits. IPOs also carry significant costs and could require the company to raise additional funding if its shares perform poorly.
Trading or investing in IPO shares can be riskier than getting exposure to established stocks, due to the unpredictability of the new listing.
How to trade or invest in an IPO
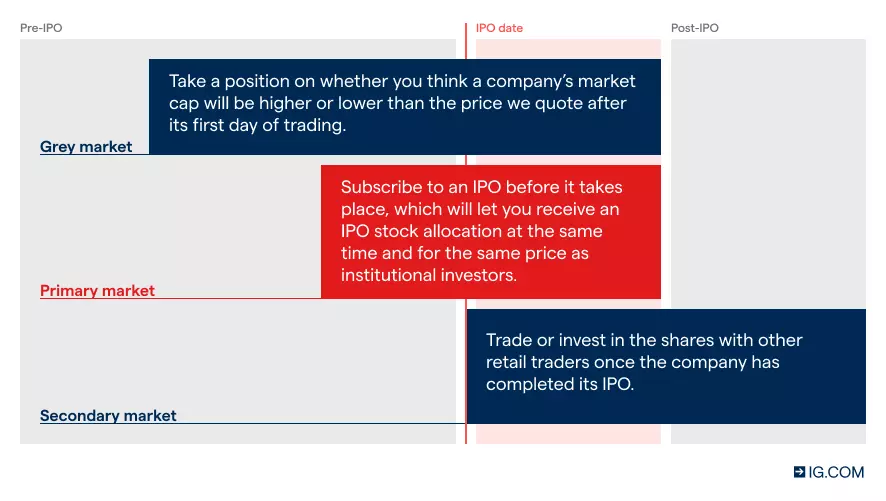
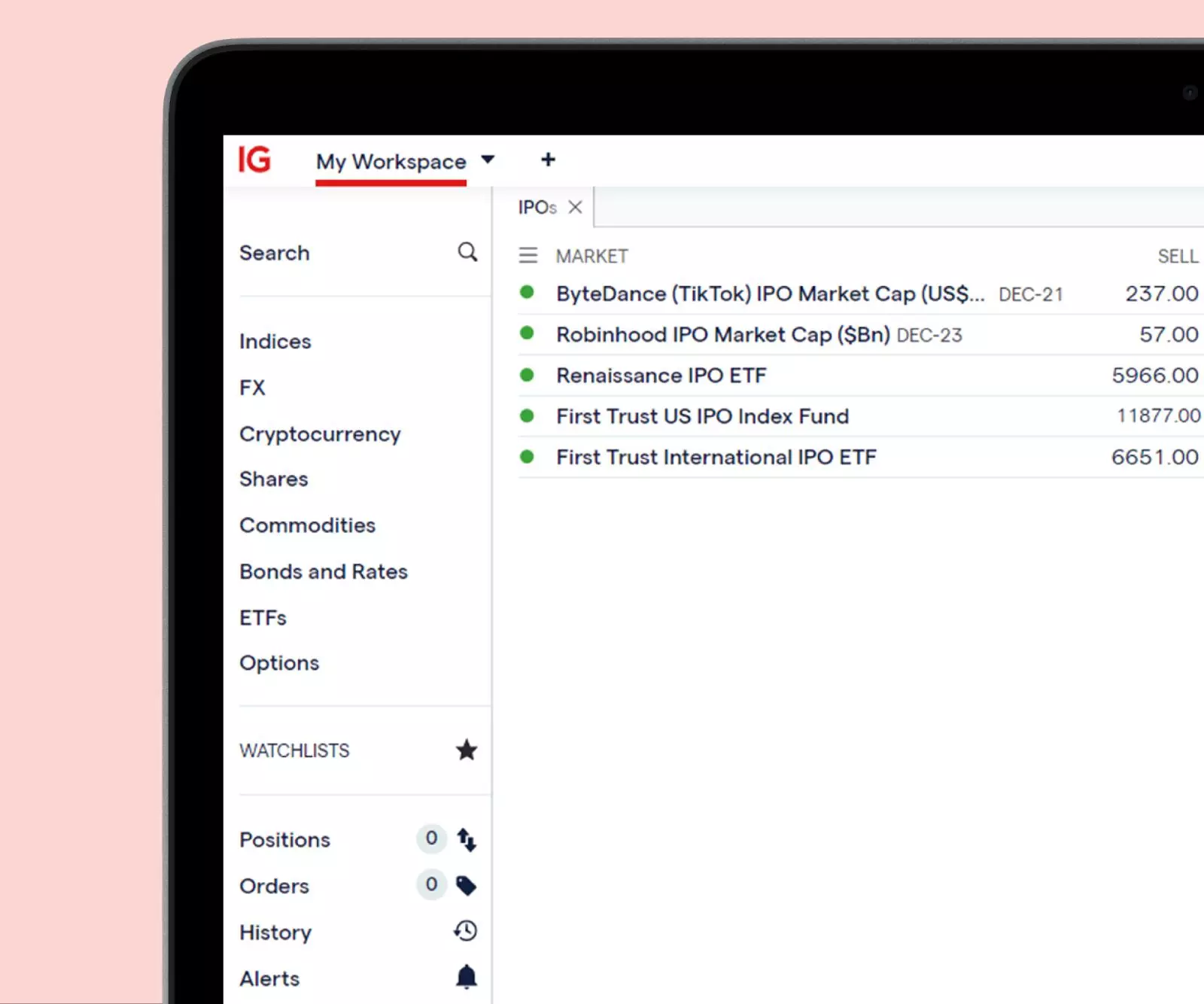
Grey markets
If a company’s IPO has a lot of public interest, we may offer a ‘grey market’ before the IPO takes place. This’ll let you speculate on the company’s estimated market cap at the end of its first trading day – and the price that we quote will be based on our prediction for the company’s market cap.
- You’ll ‘buy’ (go long) if you think the company’s market cap will be higher than the price shown
- You’ll ‘sell’ (go short) if you think the company’s market cap will be lower than the price shown
When you speculate on IPO shares with us, you’ll be doing so by means of CFDs or spread bets. This gives you exposure to the share price without you taking ownership of shares in that company.
CFDs and spread bets are leveraged, meaning you’ll get increased market exposure for a small deposit – rather than paying the entire value of the position upfront. However, your profit or loss will be determined by the total size of your position and can far outweigh your deposit amount, often making trading IPOs higher risk than taking ownership of shares directly.
Primary market: buying at the IPO price
You can subscribe to the IPO ahead of the offering through our partnership with PrimaryBid.2 By subscribing to the IPO, you’ll receive a stock allocation on the primary market, at the same time and price as institutional investors, in the primary market. This means you don’t need to wait for the secondary market to open in order to take your position.
*Note: Primary market and grey market IPO trading are not available with us
Secondary market
Once an IPO is complete, you can start trading or investing in shares on the secondary market. With us, you’ll be able to:
- Go long or short on share prices with contracts for difference (CFDs)
Remember, if you’re trading, you can profit from upward or downward share price movements.
How do companies perform after their IPO?
The tables below show how companies’ share prices performed after the first day, first week, and first month of their IPOs.
- First day
- First week
- First month
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2017-2020 | |
| All IPOs | 8.6% | 8.7% | 8.5% | 6.6% | 8.3% |
| Main market | 6.3% | 5.7% | 7.4% | 4.6% | 6.1% |
| AIM | 11.2% | 12.1% | 10.7% | 9.0% | 11.2% |
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2017-2020 | |
| All IPOs | 9.3% | 10.3% | 11.0% | 9.0% | 9.8% |
| Main market | 5.6% | 4.8% | 9.4% | 4.4% | 5.9% |
| AIM | 13.6% | 16.5% | 14.3% | 14.6% | 14.7% |
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2017-2020 | |
| All IPOs | 8.0% | 9.5% | 13.9% | 1.5% | 8.4% |
| Main market | 5.3% | 2.8% | 13.7% | -0.7% | 5.2% |
| AIM | 11.0% | 17.3% | 14.2% | 4.2% | 12.4% |
FAQs
How long is the IPO process?
The length of the IPO process can vary, depending on how well it’s being managed and coordinated. The financial audit stage – which is the first stage of a company going public – can be the longest, especially if the company’s books are not in order.
To combat the time commitment of a traditional IPO, more and more companies are turning to alternative methods of going public, like special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) – which can be considerably faster.
How much does an IPO cost?
The cost of an IPO for a company will depend on the registration requirements of the stock exchange where it’s being listed. In addition, there will generally be underwriting fees and offering costs, as well as legal and accounting fees. Larger companies could face additional costs when preparing to list.
How is the IPO price calculated?
The IPO price is calculated by an investment bank. First, the company decides how many of its shares it wants to sell to the public. Then, the nominated investment bank does a thorough valuation of the business. Once that’s done, an initial share price is released, and the public can start trading shares when the listing happens.
Develop your knowledge of financial markets
Find out more about a range of markets and test yourself with IG Academy’s online courses.
Try these next
Find out more about trading shares
Learn how to make the most of IPOs
Discover how to buy and trade shares
