What are indices and how do you trade them?
Indices measure the performance of a group of stocks. Discover everything you need to know about stock indices, including how to trade them and which markets are available to you.
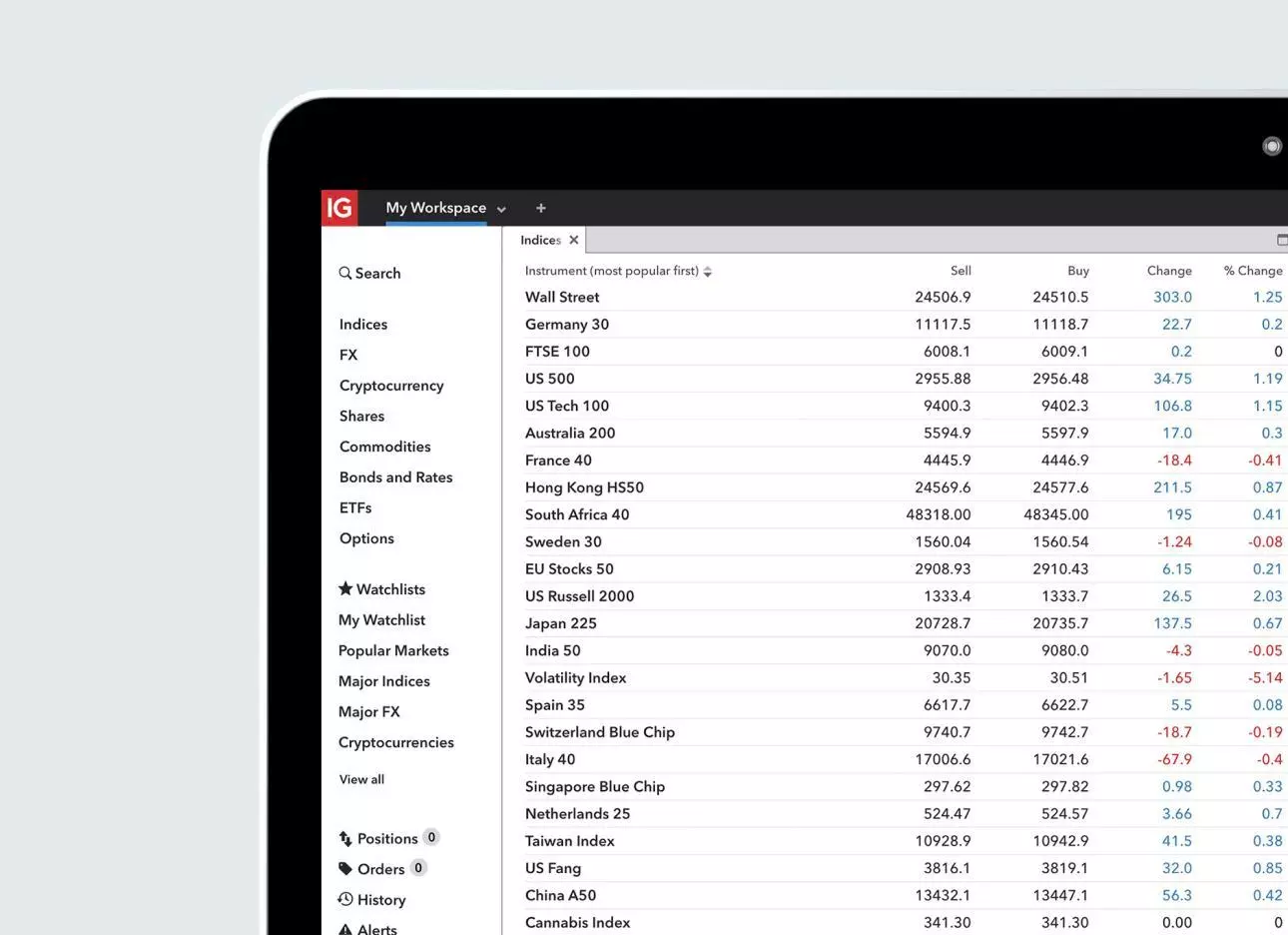
What are indices?
Indices are a measurement of the price performance of a group of shares from an exchange. For example, the FTSE 100 tracks the 100 largest companies on the London Stock Exchange. Trading indices enables you to get exposure to an entire economy or sector at once, while only having to open a single position.
You can speculate on the price of indices rising or falling without taking ownership of the underlying asset with CFDs. Indices are a highly liquid market to trade, and with more trading hours than most other markets, you can receive longer exposure to potential opportunities. Start trading indices today with an IG account.
How are stock market indices calculated?
Most stock market indices are calculated according to the market capitalisation of their component companies. This method gives greater weighting to larger cap companies, which means their performance will affect an index’s value more than lower cap companies.
However, some popular indices – including the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) – are price-weighted. This method gives greater weighting to companies with higher share prices, meaning that changes in their values will have a greater effect on the current price of an index.
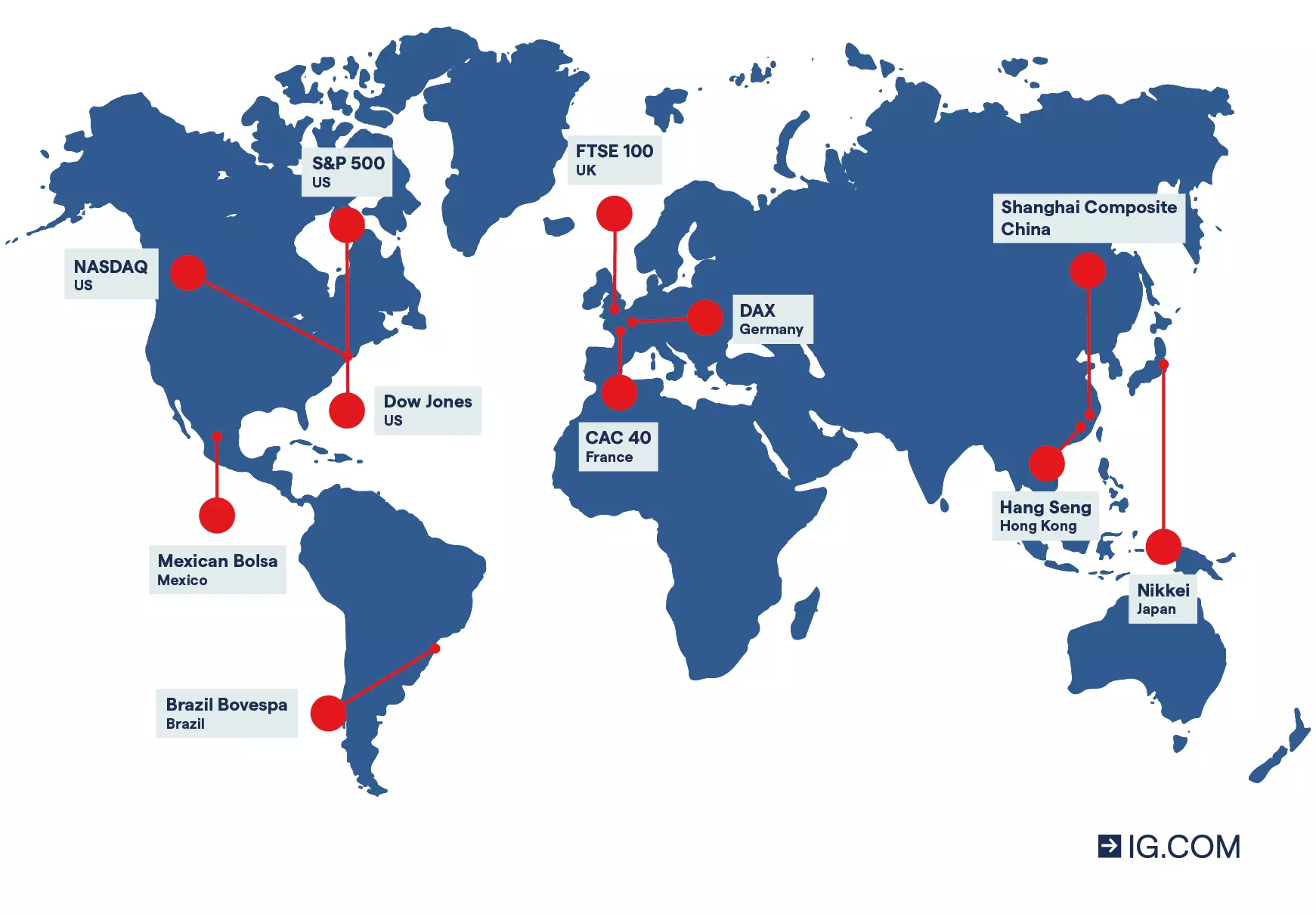
What are the most traded indices?
- DJIA (Wall Street) – measures the value of the 30 largest blue-chip stocks in the US
- DAX (Germany 40) – tracks the performance of the 30 largest companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange
- NASDAQ 100 (US Tech 100) – reports the market value of the 100 largest non-financial companies in the US
- FTSE 100 – measures the performance of 100 blue-chip companies listed on the London Stock Exchange
- S&P 500 (US 500) – tracks the value of 500 large cap companies in the US
How to identify what moves an index’s price
An index’s price can be affected by a range of factors, including:
- Economic news – investor sentiment, central bank announcements, payroll reports or other economic events can affect underlying volatility, which can cause an index’s price to move
- Company financial results – individual company profits and losses will cause share prices to increase or decrease, which can affect an index’s price
- Company announcements – changes to company leadership or possible mergers will likely affect share prices, which can have either a positive or negative effect on an index’s price
- Changes to an index’s composition – weighted indices can see their prices shift when companies are added or removed, as traders adjust their positions to account for the new composition
- Commodity prices – various commodities will affect different indices’ prices. For example, 15% of the shares listed on the FTSE 100 are commodity stocks, which means any fluctuations in the commodity market could affect the index’s price
Get immediate exposure to an entire index
A primary advantage of trading indices using derivatives like spread bets and CFDs is the sheer breadth of market exposure accessed in a single position.
Indices, as a representation of an entire market or industry, measure the overall performance of all stocks included within the index. For example, let’s say a notable event occurs that affects the market as a whole rather than just a few specific companies. By taking a position on an index like the S&P 500, you trade on how the incident will impact a wide cross-section of the most important stocks in an economy or sector.
When you trade an index in this way, you also take your position at the exact price of the market at the time you trade, minus any charges incurred.
To gain a similar level of exposure through traditional investments, you’d have to incur the time and monetary costs of purchasing the individual shares making up the index, or invest in an exchange traded fund (ETF), which would be priced according to the fund's net asset value.
Simply put, indices trading is an immediate and direct way to trade on the movements of the total market at its current price.
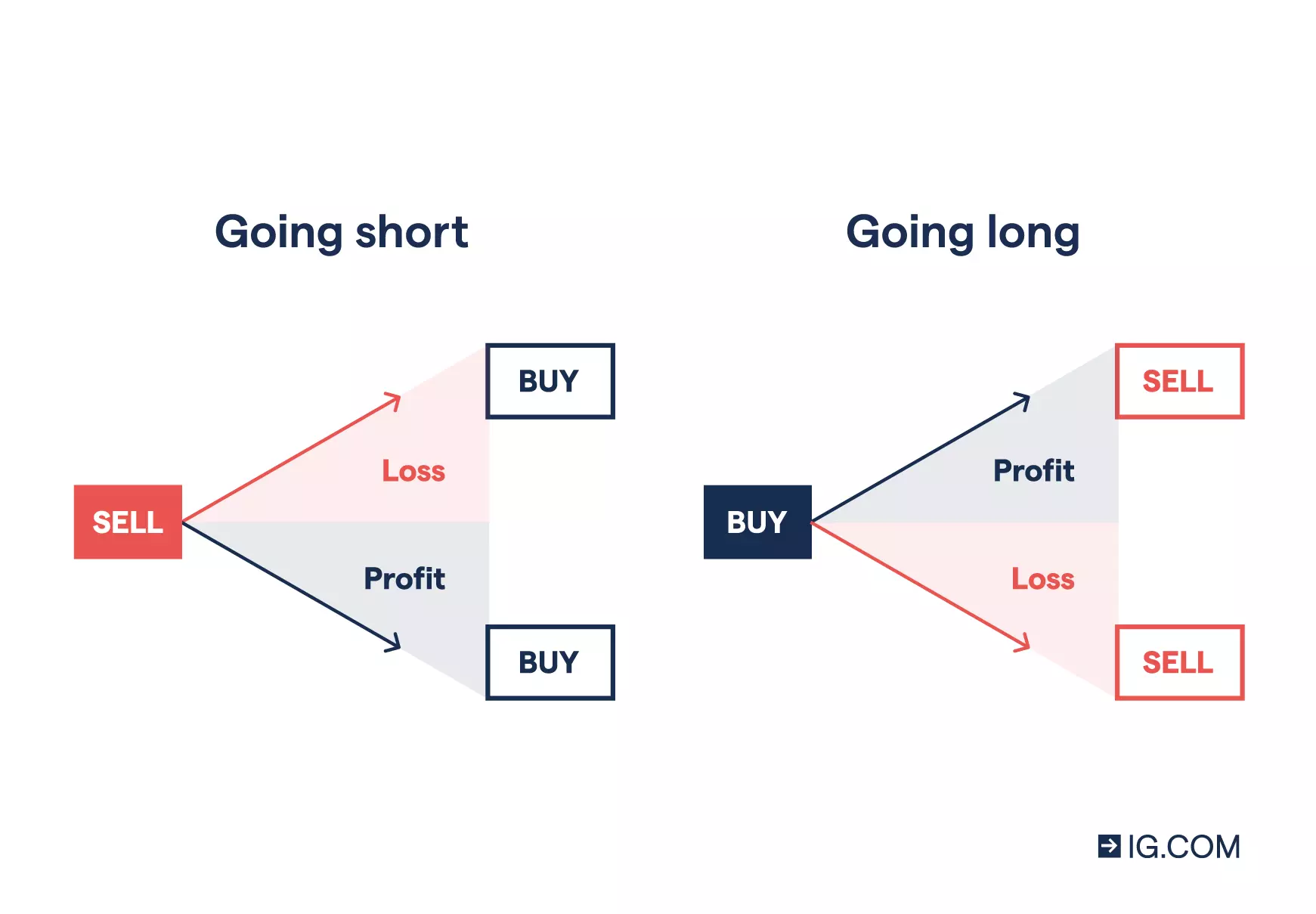
Go long or short on an entire index
When index trading with CFDs, you can go both long and short. Going long means you’re buying a market because you expect the price to rise. Going short means you’re selling a market because you expect the price to fall.
With CFD trading, your profit or loss is determined by the accuracy of your prediction and the overall size of the market movement.
Trade with leverage
CFDs are leveraged products. This means you only need to commit an initial deposit – known as margin – to open a position that gives you much larger market exposure.
When trading with leverage, you should remember that your profit or loss is calculated using the entire position size, not just the initial margin used to open it.
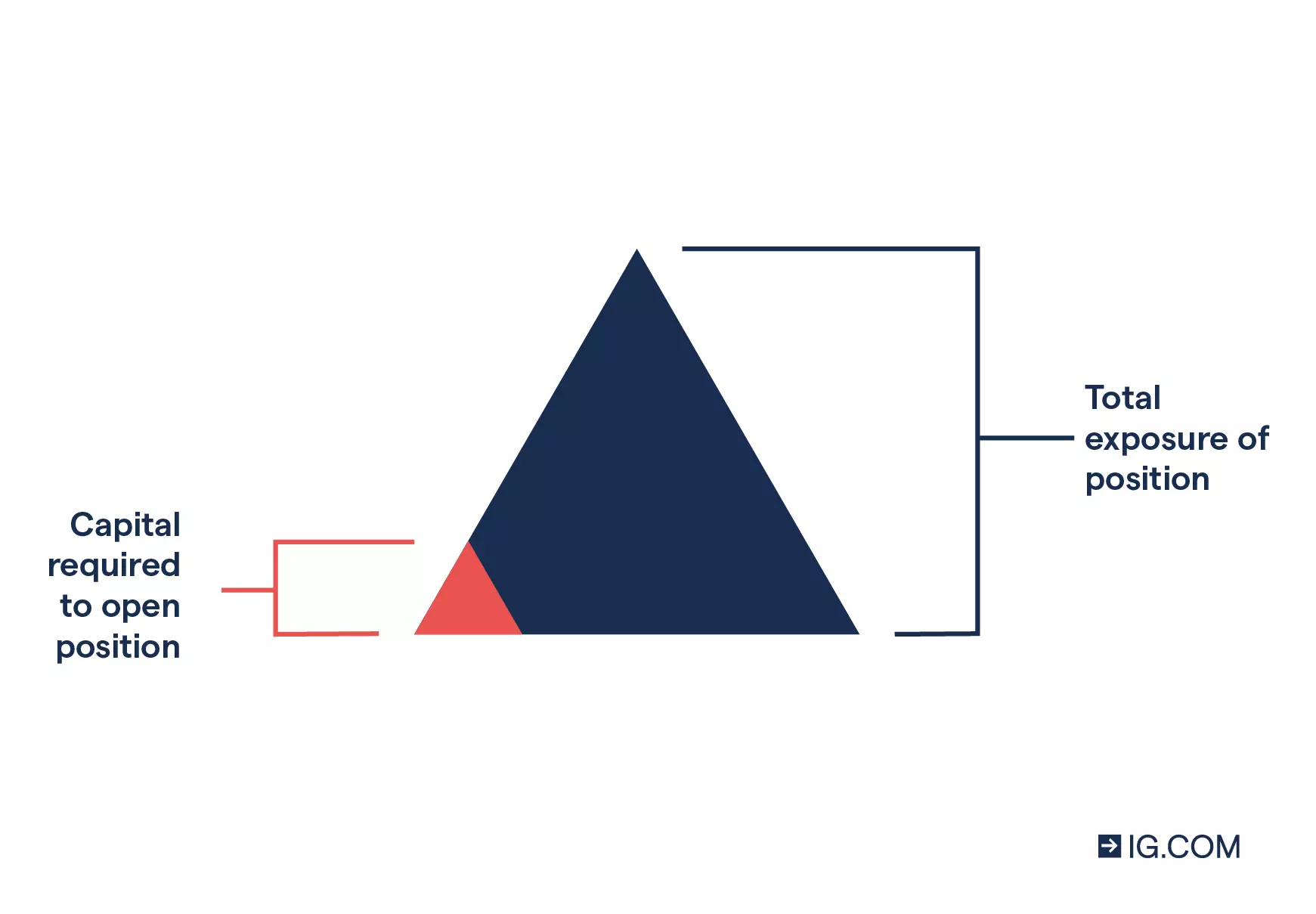
Hedge your existing positions
An investor with a collection of different shares might short an index to protect themselves from losses in their portfolio. If the market enters a downturn and their shares start to lose value, the short position on the index will increase in value – offsetting the losses from the stocks. However, if the stocks increased in value, the short index position would offset a proportion of the profits which had been made.
Alternatively, if you had a current short position on several individual stocks which feature on an index, you can hedge against the risk of any price increases with a long position on that index. If the index rises, your index position will earn a profit, counteracting a proportion of the losses on your short stock positions.
Trade indices with CFDs
With us, you can trade indices via CFDs. This products are financial derivatives, which means you can use them to speculate on indices that are rising in value, as well as falling.
CFDs
CFDs are a contract between two parties to exchange the difference in price from the point at which the contract is opened, to the point at which it is closed.
| CFDs trading | |
| Main benefits | Go long or short |
| Accesible to | All clients |
| Tradable in | Contracts which mirror the price movements in the underlying market |
| Commission | Commision-free |
| Platforms | Web platform, mobile trading app and MT4 |
| Learn more |
Decide whether to trade cash indices, futures or options
When you trade with IG, there are two ways to get exposure to an index’s price: by trading cash indices or index futures.
Cash indices
Cash indices are favoured by traders with a short-term outlook – such as day traders – because they have tighter spreads than index futures. Cash indices are traded at the spot price – which is the current price of the underlying market.
Many traders will close their cash indices positions at the end of the trading day and open new positions the following morning to avoid paying overnight funding charges.
Index futures
Index futures are often preferred by traders with a long-term market outlook. This is because, while they have wider spreads than cash indices, the overnight funding charge is included. Index futures are traded at the futures price – the price that futures traders agree in the present for delivery in the future.
If you plan on holding on to an index position for a long time, trading index futures will mean that you don’t incur frequent overnight funding charges.
Index options
When you trade options with us, you’ll be using spread bets or CFDs to speculate on an option’s premium – which will fluctuate as the probability of the option being profitable at expiry changes. Owing to their complexity, options trading is often only recommended for experienced traders.
Additionally, please bear in mind that there is substantial risk when selling options. Selling a call, for example, incurs potentially unlimited risk as market prices can keep rising – theoretically, without limit.
- CFDs
| Min. cash spread | Min. futures spread | |
| Wall Street | 1.6 | 6 |
| Germany 40 | 1 | 6 |
| US Tech 100 | 1 | 3 |
| FTSE 100 | 1 | 4 |
| US 500 | 0.4 | 1 |
ETFs and shares
Aside from cash indices and index futures, you can also trade index ETFs and individual shares with IG. Again, you can open these positions with CFDs. If you’d rather take ownership of the underlying market, you can also invest directly in index ETFs and individual shares with IG.
Create an account and log in
To start trading indices with CFDs today, open an account with IG. We’re a FTSE 250 company with over 45 years’ experience. Our spreads are among the lowest in the industry, and we have a larger offering of weekend index markets than any other UK provider.
Select the index you want to trade
It’s important to choose an index that’s best-suited to your trading style. This will depend on your individual appetite for risk, available capital and whether you prefer taking short-term or long-term positions.
For example, the Germany 40 is usually a volatile index which is favoured by traders with high risk appetites and who prefer short-term trading. On the other hand, the US 500 is largely known for its steady returns over time, making it a favourite with traders with lower appetites for risk and a long-term outlook.
IG offers over 80 index markets on both major and minor global indices1, meaning that you’re more likely to find a market that fits your individual trading style.
- Major indices
- Minor indices
Decide whether to go long or short
Going long means that you are speculating on the value of an index increasing, and going short means that you are speculating on its value decreasing.
If the economic outlook for an economy or sector looks good based on the performance of the companies on an index, a long position could help you realise a profit if the index increased in value.
If the outlook is poor – possibly because large companies on a capitalisation-weighted index are underperforming – you might want to go short on the expectation that the index will fall in value.
Set your stops and limits
Stops and limits are essential tools for managing your risk while trading indices. A stop order will close your position automatically if it goes to a less favourable level than the current market price, while a limit order will close your position automatically if it goes to a more favourable market price.
Open and monitor your trade
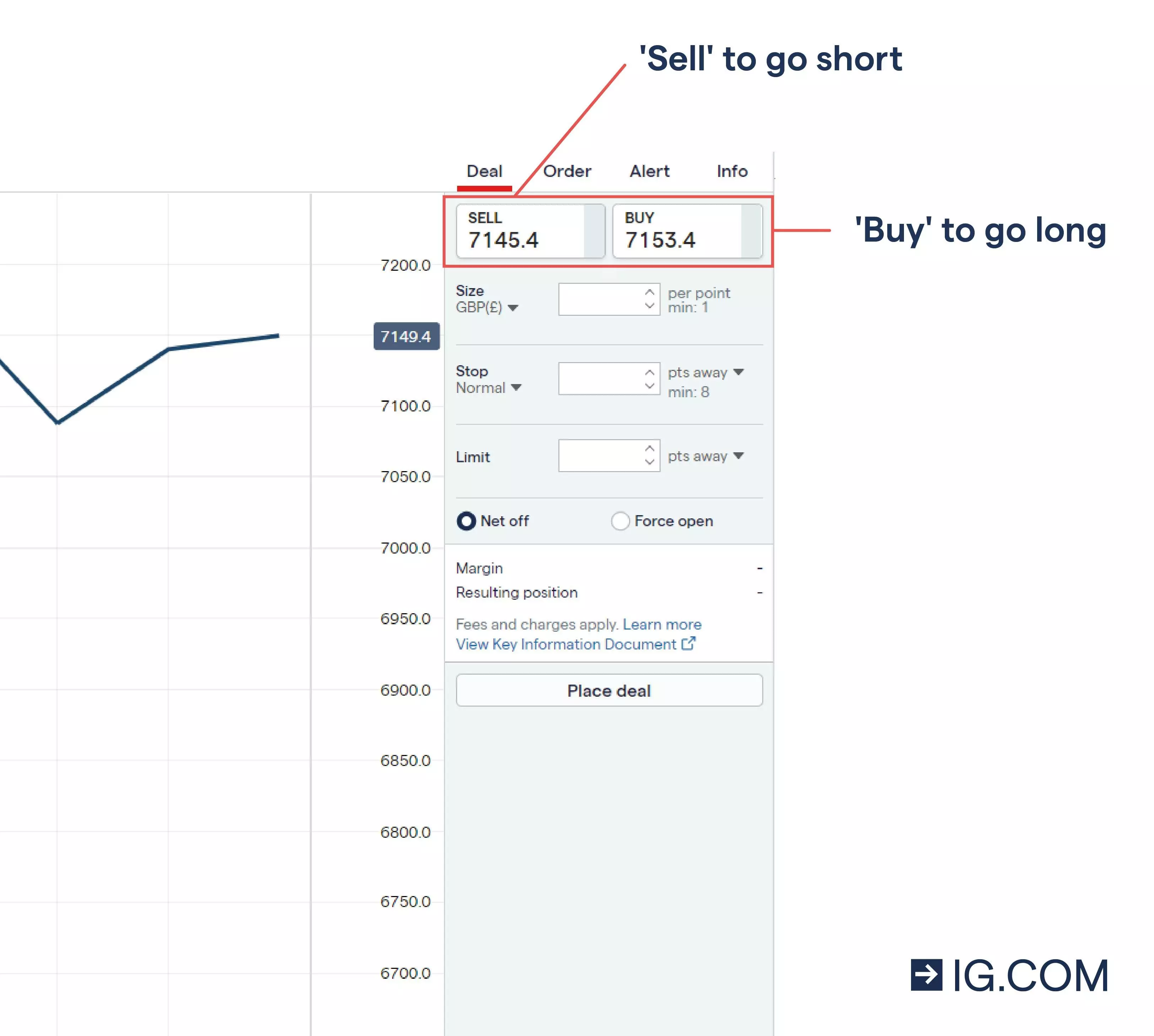
When you think you’re ready to start indices trading, it’s time to open your trade. To do this, go to the market you want to trade on the IG trading platform – Wall Street for example.
Next, decide whether you want to deal at the cash price or the futures price – and select buy if you think the price will rise, or sell if you think the price will fall. Enter your position size, and click ‘place deal’ to open your trade.
Monitor your position, and close your trade when you want to take a profit or cut a loss.
FAQs
What does indices trading mean?
Indices trading means that you are taking a position on a stock index – which is measure of the performance of several different companies. Indices trading can be a way to get exposure to an entire sector or economy at once, without having to open positions on lots of different shares.
Can I profit from index trading?
You can profit from index trading by accurately predicting an index’s price movements. For example, if you think the FTSE 100 will rise, you would open a long position. But, if you think it will fall, you would open a short position. Your profit or loss is determined by the extent to which your forecast is correct.
What does it mean to buy index futures?
To buy index futures means that you are opening a long position on an index because you think the price will increase. If you are correct in your forecast, you will profit, but if you are incorrect, you will incur a loss.
Are index futures derivatives?
Index futures are a financial derivative. Their price is based on the price in an underlying market, which is influenced by supply, demand and volatility. You can speculate on index futures with CFDs, and they will be traded at the futures price – meaning that you won’t incur overnight funding charges.
How can risk be hedged with stock index futures?
You can hedge risk with index futures by taking a position that will turn to profit if one or more of your existing positions starts to lose money. For example, if you held long positions on a selection of US tech stocks, you could open a short position on the US Tech 100 to offset any losses you might incur from the shares declining in value.
Alternatively, if you held short positions on a collection of large-cap UK shares, you could open a long position on a FTSE 100 index future to protect yourself against any possible increases in the price of the underlying shares.
Can I sell futures before expiry?
You can sell futures before expiry, and many traders will exit their positions before the expiry date arrives. To do so, you can sell your contract outright or purchase an opposing contract which cancels out your current position.
Develop your knowledge of financial markets
Find out more about a range of markets and test yourself with IG Academy’s online courses.

Develop your knowledge of financial markets
Find out more about a range of markets and test yourself with IG Academy’s online courses.
Try these next
Find out how to trade the VIX and speculating on rising or falling volatility
Discover IG’s offering of over 16,000 international shares
Learn how to buy and trade shares – including the differences between each
1 IG offers 81 indices markets for CFD trading
